Seoses kasvava vajadusega varukoopiate järgi tegin endale selgeks, kuidas bash scripti kasutada. Mul olid varasemalt vajalikud read olemas ja sain neid terminalis kasutada aga selline rea kaupa toimetamine muutus tüütuks. Google otsing andis sellised vastused:
Aga noh, natuke liiga keerulised minu arust. NB! Kui SSH ühenduse loomine on sulle võõras, siis Zone helpis on hea juhend. Aga, sul tegelikult ei ole SSHd varukoopia tegemiseks vaja. Piisab ka komplektist: notepad + FTP + cron töö (iseteeninduses). Samas, katsetamiseks ja hiljem nt lahtipakkimiseks on siiski SSH mugavam.
📌 NB! See varukoopia tegemise juhend töötab standardse WP installi puhul. Muudel juhtudel (nagu näiteks see) ma ei ole seda katsetanud.
Scripti sisu
Echo asjad panin tooltipideks, et terminalis vaikus ei oleks terve aja 🙂 Kui andmebaas on suur, siis selle export ja pakkimine võtab omajagu aega. Eeldus on, et scripti fail on ühe kausta jagu madalamal kui WP install. Antud näites on WP install kaustas /htdocs.
#!/bin/bash echo "Backupi tegemine algas!" cd htdocs echo "Andmebaasi export algas..." wp-cli db export echo "" echo "Andmebaasi export tehtud!" cd .. echo "Alustasin pakkimist..." tar czf "$(date +"%Y%m%d")_veebileht.tar.gz" htdocs/ echo "Pakkimine tehtud!" rm htdocs/*.sql echo "Andmebaas kustutatud!" echo "Backupi tegemine lõpetatud."
Selle ülal oleva sisu salvestad näiteks backup.sh failina, käivitad eelpool toodud käsureaga ja ongi kõik. Mida mingi rida teeb?
3. rida – liigub kausta, kus on WP install.
5. rida – teeb andmebaasist koopia ja paneb selle WP installi kausta. Zones piisab wp db export, Veebimajutuses on vaja wp-cli db export.
6. rida – prindib tühja rea terminali 🙂 ilu pärast.
8. rida – liigub ühe kausta jagu madalamale
10. rida – teeb tar.gz formaadis koopia WP installi kaustast, kus sees on ka andmebaasi koopia. Faili nimi kujul YYYYMMDD_failinimi.tar.gz. Kui peaksid selle varukoopia tegemise näiteks cron tööga automatiseerima, siis iga päev on erinev faili nimi. Stackoverflowst leiab mingi juhendi, kuidas kellaaeg ka sisse panna soovi korral.
12. rida – kustutab andmebaasi koopia (kõik *.sql failid WP installi kaustast), sest noh, ei jäta selliseid asju vedelema.
NB! Zones ei sellist lihtsat varianti .sh käivitamiseks nagu pildil näidatud. Seal on vaja faili 2. reale lisada ${0%/*} või 3. reale panna täielik teekond alates /tmp kaustast, kus script tegelikult käivitatakse. Lisaks on käsk iseteeninduses selline:
/bin/bash [[$D2ND_A]]/script.sh
ja scripti failile on vaja teha terminalis: chmod +x script.sh (sest script peab olema executable)
Veelkord: See path, mis Zone iseteeninduses määrad on täispikk kataloog, kus script asub. Sinna ei tehta vaikimisi “cd”, see on lihtsalt muutuja, mida kasutada, et näiteks kui partitsioon peaks muutuma, siis muutujas läheb partitsioon ise õigeks. Cron käivitatakse ~/tmp kataloogis. Käsurealt võib proovida ise cd ~/tmp ja seal sees /data/…/script.sh käivitada. See on siis sama olukord, nagu crontab seda käivitaks.
Kuidas .sh faili teha?
Notepadiga teed faili (kui muud tööriista ei ole harjunud kasutama) ja hiljem muuda lihtsalt faili laiend ära 🙂
Scripti käivitamine
Käsk scripti käivitamiseks (koos sisselogimisega) on Zones selline:
ssh virt5713@neti.ee "bash domeenid/www.neti.ee/neti.sh"
Veebimajutuses selline:
ssh -p 1022 vhost57175ssh@pood.eu "bash pood.sh"
.sh faili path sõltub sellest, kuhu sa parasjagu sisse logimisega satud. Zone.ee ja Veebimajutuse käsud on pisut erinevad (aga mõlemal on iseteeninduses juhendid olemas. See teeb korraga sisselogimise ja scripti käivituse. Kui oled juba sisse loginud ja .sh failiga samas kaustas, siis piisab lihtsalt:
bash failinimi.sh
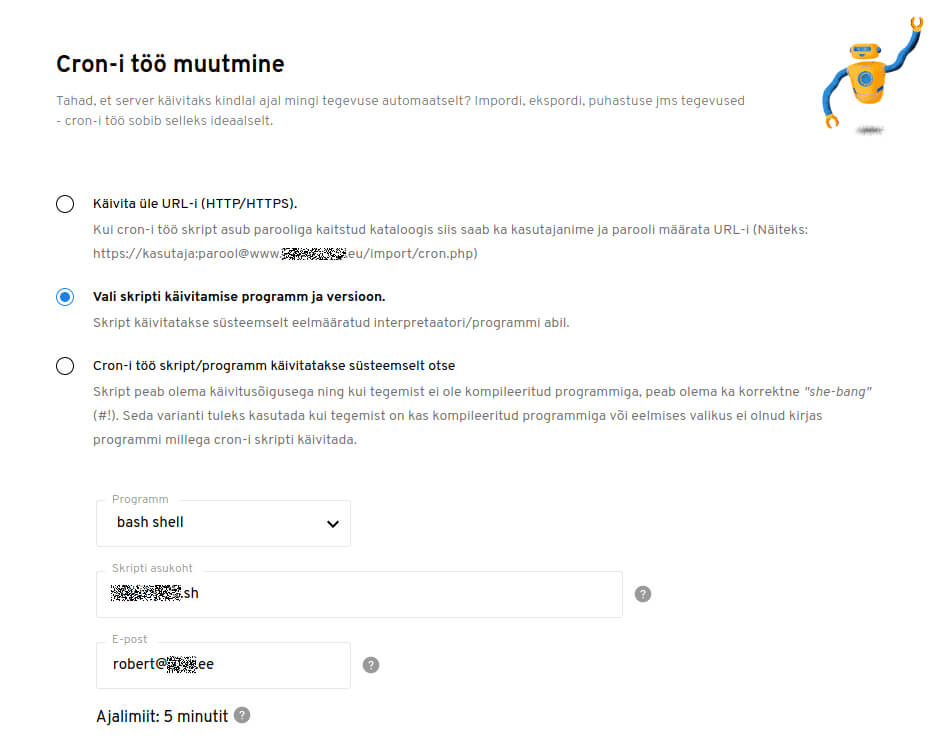
Regulaarse varukoopia tegemiseks (nt üle päeva) on hea mõte kasutada regulaartöid ehk cron töid, mida on lihtne seadistada iseteenindusest. See tähendab, et script pannakse tööle sinu poolt määratud ajal. Veebimajutuses näeb see välja näiteks nii.
Kuidas lahti pakkida
Lahti pakkimise osa on mul siin olemas käsuridade kaupa. Win10 arvutis mul seda lihtsalt 7zipiga näiteks lahti pakkida ei õnnestunud aga serveris tuleb kenasti näiteks sellise käsureaga:
tar -xzvf archive.tar.gz dir/
Kuidas kokku pakkida (excludega)
tar -zcvf "$(date +"%Y%m%d")_occo.tar.gz" --exclude=node_modules occo/
NB! Suurte failihulkade lahtipakkimisel ole ettevaatlik. Ma ükskord pakkisin Magento (~60 tuhat faili) serveri root folderisse lahti muude asjade sekka. Tükk aega oli koristamist 😀